2. Policy Assessment
Using developed mathematical models, we assess different guideline/policies.
Using our developed mathematical models, we evaluate the effectiveness and impact of various guidelines and policies related to infectious disease prevention, control, and treatment. This includes assessing strategies such as vaccination protocols, quarantine and isolation measures, antiviral treatments, and public health interventions. By simulating different scenarios, we aim to provide data-driven insights to optimize policy decisions, improve healthcare resource allocation, and enhance preparedness for emerging infectious threats.
As an example, we have compared different isolation guidelines for COVID-19.
Isolation of COVID-19 patients has been implemented in most countries since the pandemic started. For example, in Singapore, isolation was recommended for 7 or 14 days for vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, which is due to the difference in viral load dynamics (i.e., viral load over the course of infection). However, except vaccination status, the current isolation guideline recommends the same length of isolation for all COVID-19 patients (the fixed-period guideline). As is suggested elsewhere, there is huge variability in viral load dynamics among individuals with the same vaccination status.
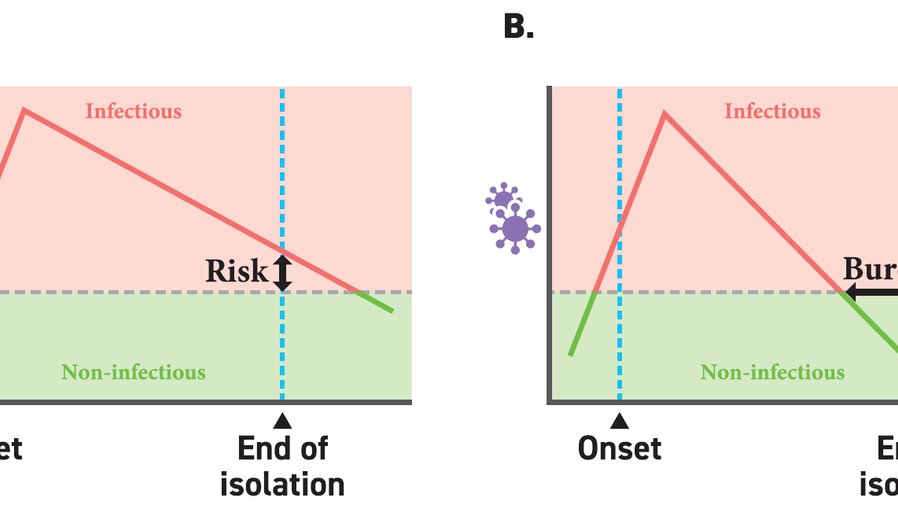
Thus, we propose different isolation guidelines accounting of the heterogeneity in viral dynamics to optimize the length of isolation each patient (or groups). For comparison of isolation guidelines, we use two metrics: the length of redundant isolation period (burden) and the probability of prematurely ending isolation (risk) (Figure). The project findings are expected to support development and assessment of different isolation guidelines in-silico. If successful, this approach can reduce both the individual and societal impact of the pandemic and to provide a framework that could be applied to other emerging or remerging infectious diseases.
Related publication:
Jeong YD†, Ejima K†*, Kim KS†, Iwanami S, Hart WS, Thompson RN, Jung IH, Iwami S*, Ajelli M, Aihara K (2024). Safe return to schools and workplaces: A modelling study to define guidelines for antigen screening in schools and workplaces to mitigate COVID-19 outbreaks. Communications Medicine.
Jeong YD†, Ejima K†*, Kim KS†, Joohyeon W, Iwanami S, Fujita Y, Jung IH, Aihara K, Shibuya K, Iwami S*, Bento AI‡, Ajelli M‡ (2022). Designing isolation guidelines for COVID-19 patients with rapid antigen tests. Nature Communications 13(1):4910
Jeong YD†, Ejima K†*, Kim KS†, Iwanami S, Bento AI, Fujita Y, Jung IH, Aihara K, Watashi K, Miyazaki T, Wakita T, Iwami S*, Ajelli M (2021). Revisiting the guidelines for ending isolation for COVID-19 patients. eLife 10:e69340